Bitumen
Natural bitumen is the thickest form of petroleum there is, made up of 83% carbon, 10% hydrogen, and lesser amounts of oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and other elements.
A petroleum product
Bitumen
- Cutback
- Penetration Grade
- Performance Grade
- Viscosity Grade
- Emulsion
- Polymer Bitumen
- Oxidized
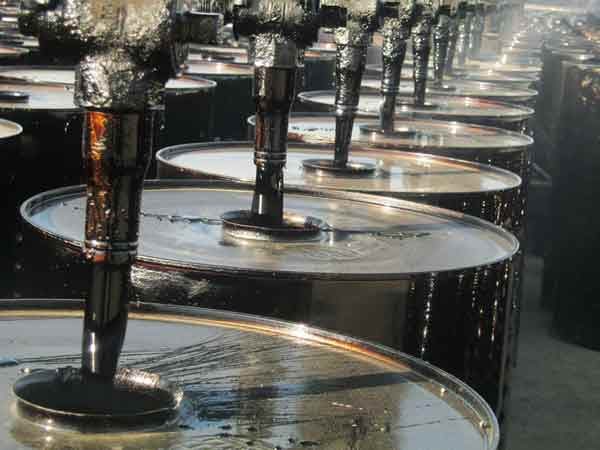








What Is Bitumen?
Natural bitumen is the thickest form of petroleum there is, made up of 83% carbon, 10% hydrogen, and lesser amounts of oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and other elements. It is a natural polymer of low molecular weight with a remarkable ability to change with temperature variations: at lower temperatures, it is rigid and brittle, at room temperature it is flexible, at higher temperatures bitumen flows.
Bitumen is a low-grade crude oil which is composed of complex, heavy hydrocarbons. In an oil reservoir, bitumen is a thick, viscous fluid and must be extracted from the ground.
When extracting it, a lot of heat and effort must be used to upgrade it to a better product. Although bitumen is hard to extract from the ground, it can bubble naturally to the surface of the Earth in petroleum seeps. These seeps are places where fossil fuels and petroleum products leak out of the Earth instead of being trapped deep below the ground. In these seeps, bitumen, asphalt, and tar bubble up into pools.
Additionally, bitumen is the main fossil fuel component of oil sands. When bitumen combines with asphaltenes a solid is formed that is useful for paving roads.

Production
In addition to being found naturally in seeps and the oil sands, bitumen can be produced by removing lighter fractions from crude oil during the refining process. Fractions that are removed are liquid petroleum gas, gasoline, and diesel.
Once crude oil has been extracted from the ground, the production of bitumen can begin. The crude oil is pumped from the storage tanks and through a system that increases the temperature of the crude oil to 200°C. The oil then moves to a furnace, where it is heated even higher to approximately 300°C where it is vaporized partially into a distillation column.
Here, the separation of the different components of crude oil occurs. As lighter components rise to the top, heavy components—including the bitumen—fall to the bottom of the column. This process is known as fractional distillation.
Finally, the bitumen is obtained by further distilling the residue in a vacuum distillation column. This type of bitumen is known as straight run bitumen.
The grade of the bitumen depends on how much volatile material remains in the distilled bitumen—with more volatiles resulting in a less pure, more liquid product

Cutback Bitumen
Cutback Bitumen is Bitumen that is dissolved in a solvent. Typical solvents include Naptha, gasoline and kerosene, white spirit, etc. The type of solvent controls the curing time while the amount determines the viscosity of the Cutback Bitumen

Penetration Grade
Penetration Grade Bitumen is a standard bitumen usually used as a Paving Grade Bitumen essential for road construction and for the production of asphalt pavements with superior properties, and it's very important once it bounds the aggregates and creates a unique cohesion and stability to the bituminous mix. Definition of bitumen penetration grade 60/70 Bitumen penetration grade 60/70 means the penetration value is in the range 60 to 70 at standard test conditions which commonly used as a Paving Grade. Bitumen is applicable for the production of hot mix asphalt for bases and pavements and for road construction.

Performance Grade
Performance Grade (PG) Bitumen is bitumen which is graded based on its performance at different temperatures. In Superpave grading system, binders are classified according to their performance in extreme hot and cold temperatures and called as performance grade (PG) bitumen.

Viscosity Grade
Known also as VG, this type of bitumen is the result of testing the viscosity level of bitumen. By this method of testing, the consistency of bitumen, meaning bitumen’s ability to flow, is measured in both 60° C and 135° C. This test temperature stands for the maximum bitumen temperature in hot summer and the temperature of bitumen when mixed. Viscosity grade bitumen was introduced in the 1970s. In order to increase the reliability of bitumen in higher temperatures and prevent the pavement from rutting, engineers identified more rational parameters (less empirical) for measuring bitumen behavior. From 1970 onwards, viscosity grading becomes popular among both traders and engineers.

Bitumen Emulsion
Bitumen emulsions provide an alternative approach in which the bitumen is liquefied by dispersing in water. Emulsions can be used with cold and wet aggregates, the final strength of the road material develops as the emulsions 'sets' – revert to a continuous bitumen phase – and water is lost. Emulsified Bitumen usually consists of bitumen droplets suspended in water. ... In the production of bitumen emulsion, water is treated with an emulsifying agent and other chemicals and is pumped to a colloid mill along with bitumen. The colloid mill breaks the bitumen up into tiny droplets.

Polymer Bitumen
Polymer modified bitumen (PMB) is one of the specially designed and engineered bitumen grades that are used in making pavement, roads for heavy duty traffic and home roofing solutions to withstand extreme weather conditions.

Oxidized Bitumen
Oxidized Bitumen or Blown bitumen grades are produced by passing air through the penetration grades. This process gives the bitumen more rubbery properties than its original formula and they are simply harder bitumen
Bitumen Use
Most refined bitumen is used in the construction industry. Mainly, it serves its use in paving and roofing applications. 85% of all bitumen is used as a binder in asphalt for roads, runways, parking lots, and footpaths. Gravel and crushed rock are mixed with thick bitumen, holding it together and it is then applied to roadways. 10% of the bitumen used worldwide is used in the roofing industry as its waterproofing qualities help make roofs function well. 5% of bitumen is used for sealing and insulating purposes in various building materials such as carpet tile backing and paint.
In addition to these main uses, bitumen also has many minor uses. Other examples are soundproofing, explosives, mildew protection, a binder in briquettes, a backing to mirrors, shoe soles, fence post coating, and soil stabilization.
Bitumen and asphalt, what’s the difference?
When people talk about asphalt and bitumen, the words are often used to describe the same thing, which is not correct. To set the record straight we offer an explanation of the difference below:
Bitumen is the liquid binder that holds asphalt together. A bitumen-sealed surface is a layer of bitumen sprayed and then covered with an aggregate. This is then repeated to give a two-coat seal. Asphalt is produced in a plant that heats, dries and mixes aggregate, bitumen and sand into a composite.
It’s all good to understand the difference between the two. However, which one is the best option for you?
Benefits and Disadvantages of Asphalt
Benefits:
- Minimal noise
- Durable with a life span of 20 + years
- Energy-efficient -reduces friction between tire and car, which in turns means better fuel economy and a reduction of carbon dioxide emission
- Safer than most pavement options- asphalt gets a smoother and more skid-resistant surface making asphalt a safer option
- Reduced wear and tear on vehicles and tires
Disadvantages:
- More expensive to install compared to bitumen
- Requires a well-prepared surface before paving is done
- Extreme hot temperatures can affect the asphalt negatively and make it go soft
Benefits and Disadvantages of Bitumen
Benefits:
- Cheap to install compared to asphalt
- Can be recycled instead of going to landfill
Disadvantages:
- The loose rocks on bitumen pavements make the driving experience noisier and wear down tires.
- Less durable
- Extreme weather and improper weather conditions tend to make bituminous pavement slick and soft.
- Can cause pollution to soil and groundwater
If you require any varieties of Bitumen and demand it to any destination port, please view our Bitumen products in below petroleum link:

